What is stomach cancer?
- Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer is a
cellular tumor that begins in
the stomach. Just behind the ribs in the top middle of the belly is where the
stomach is located.
Food digestion and breakdown are facilitated by
the stomach. Any area of the
stomach has chance of developing stomach cancer. The primary portion of the
stomach is where the stomach cancer occurs in the majority of the world. The
partis called the stomach.
In the United States, the gastroesophageal
junction is where stomach cancer is
more prone to begin. This is where the stomach joins the lengthy tube that
carries food you swallow. The tube that transports food to the stomach is
called esophagus.
If the cancer is limited to the stomach,
treatment for it is more likely to be
effective. For those with minor stomach malignancies, the outlook is favorable.
Many Can anticipate getting well. When the disease is advanced and a cure is
less feasible, stomach cancers are typically discovered. It is more difficult to
treat stomach cancer when it penetrates the stomach wall or spreads to other
body areas.
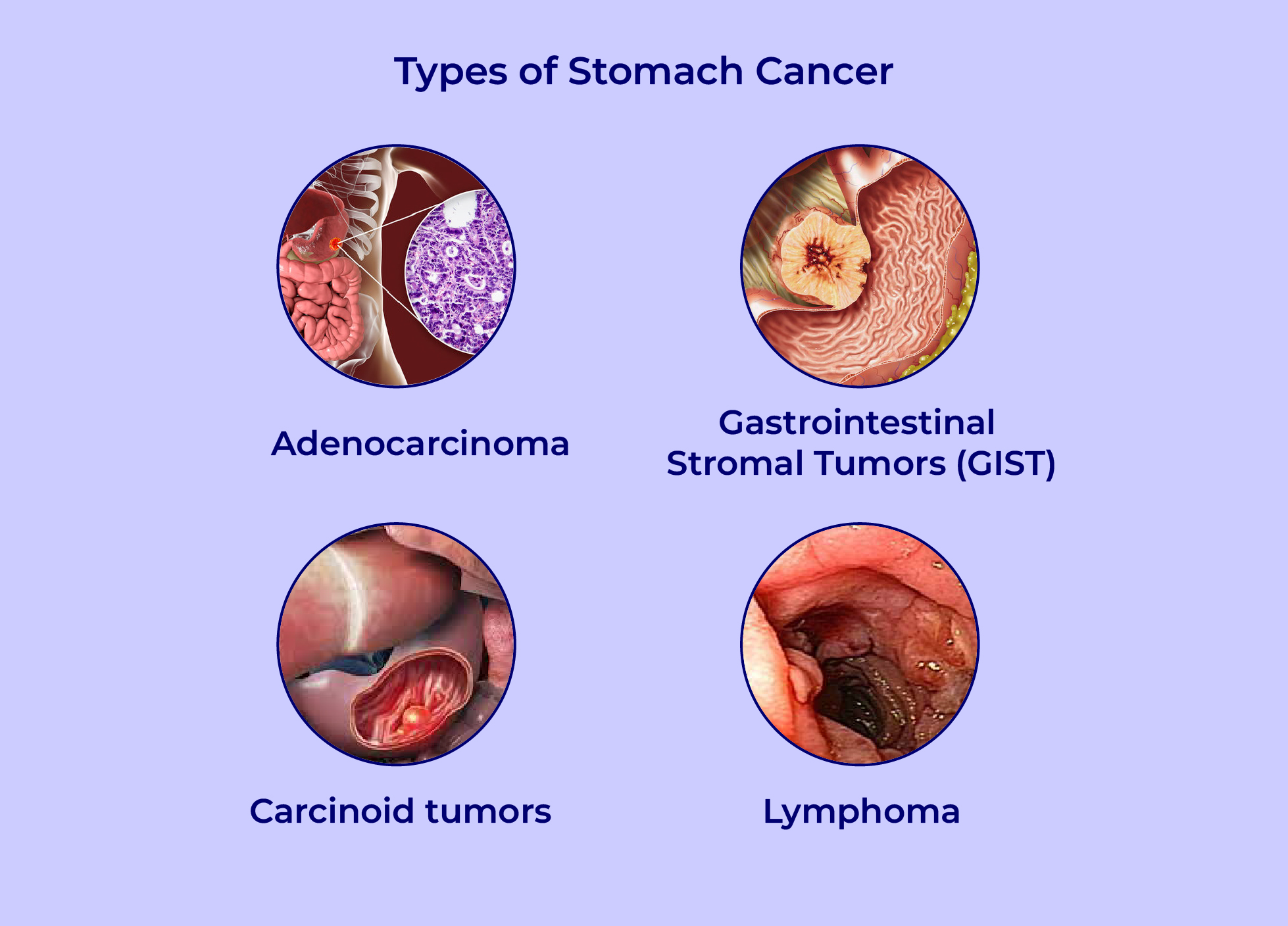
The type of stomach cancer is determined by the type of cell that gave rise to
it. Types of stomach cancer include, for instance:
-
Adenocarcinoma: Stomach cancer with an adenocarcinoma origin in
mucus-producing cells. The most typical form of stomach cancer is this
one. Adenocarcinoma stomach cancer make up the majority of
malignancies that begin in the stomach.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): Special nerve cells located in
the stomach wall and other digestive organs are where GIST begins. A
kind of soft tissue sarcoma is GIST.
- Carcinoid tumors: Neuroendocrine cells are the origins of carcinoid
tumors which are malignancies. Numerous locations across the body
contain neuroendocrine cells. They perform some of the duties if nerve
cells and some of the duties of hormone-producing cells.
Neuroendocrine tumors include carcinoid tumors.
- Lymphoma:A malignancy that begins in immune system cells is
lymphoma. The immune system of the body fights pathogens. If the
body sends immune system cells to the stomach, lymphoma may
occasionally begin there. If the body is attempting to fight off an illness,
this could occur. If the body is attempting to combat an illness, then this
might occur. Non-lymphoma Hodgkin’s is the most common type of
lymphoma that begins in the stomach.
Signs and symptoms:
The stomach cancer signs and symptoms might include:
-
Trouble swallowing
- Belly Pain
- Feeling bloated after eating
- Feeling full after eating small amounts of food
- Not feeling hungry when you would expect to be hungry
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Black stools
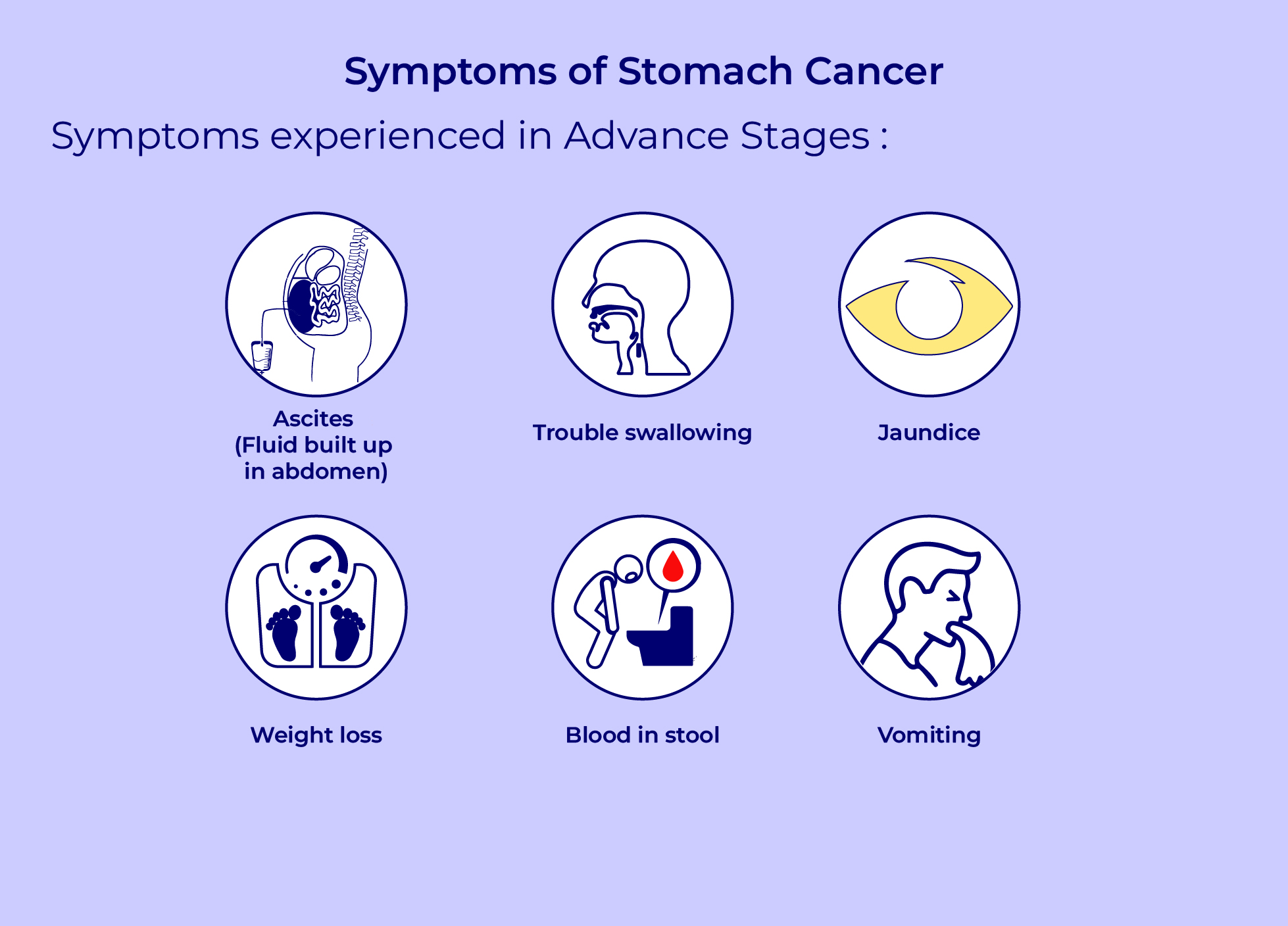
- Signs of early stomach cancer are not always
present. Indigestion and
soreness in the upper abdomen are possible symptoms when they occur.
The symptoms don’t appear until the cancer has spread. The symptoms in
the later stages of stomach cancer include extreme fatigue, unintentional
weight loss, blood vomiting and black stools.
Metastatic stomach cancer refers to stomach
cancer that has migrated to
additional bodily locations. According to its spread, it exhibits certain
symptoms. For instance, lumps may be felt through the skin if cancer
spreads to the lymph nodes. The skin and eye whites may turn yellow as a
result of cancer that has gone to the liver. It’s possible for the belly to fill
with fluids if cancer spreads there. The stomach may appear bloated.
Risk Factors
Stomach cancer risk factors include the following:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a chronic condition marked by
recurrent issues with stomach acid esophageal reflux consuming a lot
of smoked and salty meals.
- Less consumption of fruits and vegetables
- Gastrointestinal infection cause by the bacteria, Helicobacter pylori
-
Gastritis is the medical term for the swelling and irritability on the
inside of the stomach
- Smoking
- Polyps, which are growth of non-cancerous cells in the stomach.
- Family history of stomach cancer
- Family history of genetic syndromes such as Lynch syndrome, juvenile
polyposis syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and familial
adenomatous polyposis which increase the risk of stomach cancer
and other malignancies
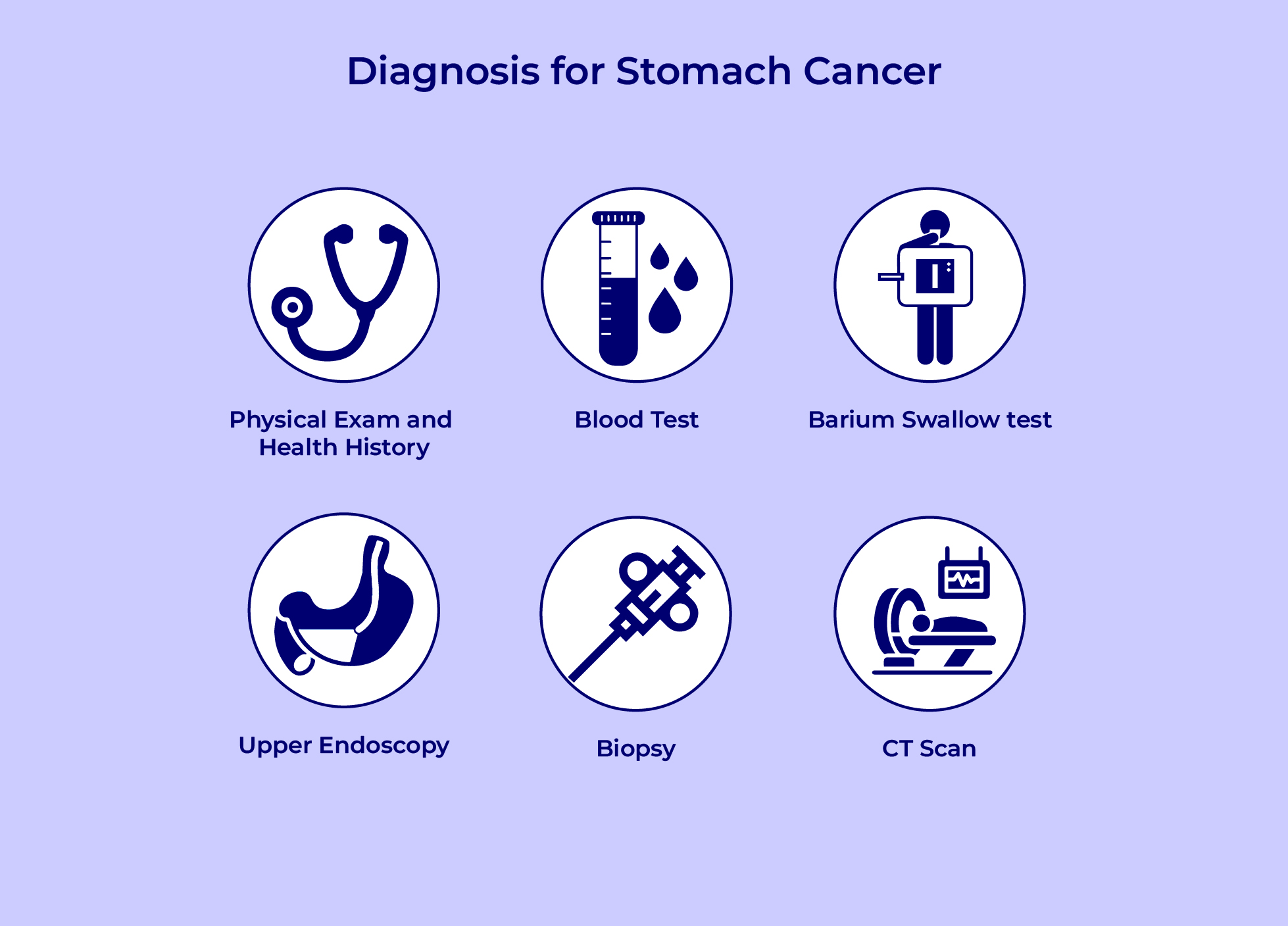
Diagnosis
The following tests and techniques are used to identify and diagnose
stomach cancer:
- Looking inside the stomach:Your doctor may insert a tiny camera
within your stomach to look for indications of cancer. This
procedure is called upper endoscopy. A thin tube with a tiny
camera on the end is passed down from the throat and into the
stomach.
- Taking a tissue sample for analysis:Your stomach may need to be
removed for testing if something that appears to be cancer is seen
there, It is known as biopsy. During and upper endoscopy, it is
possible to obtain the tissue sample, specialized tools are passed
through the tube. For testing, the sample is delivered to a lab.
- If you are diagnosed with stomach cancer, you may have additional
testing to determine whether the disease has spread. The cancer is
staged using this information. This stage provides information to your
doctor regarding the prognosis and how far along your cancer is. The
following tests and methods are used to determine the stage of
stomach cancer:
- Blood Tests
- Ultrasound
- Imaging tests
- Surgery
Prevention
- Eating a lot of fruits and vegetables will reduce your chances of
stomach cancer. Incorporate fruits and vegetables into your diet
on a daily basis. Pick a selection of fruit and vegetable colors.
- Limit your intake of smoked and salty foods. Limiting these meals
will help to protect your stomach.
- Quit smoking: Quit smoking if you do so. Stop smoking if you don’t
already. Smoking raises your risk of developing stomach cancer as
well as several other cancers. Ask your doctor for assistance if you
need it because quitting smoking can be difficult.
- In case stomach cancer runs in your family, let your doctor know.
People who have a strong family history of stomach cancer may
undergo screening can find stomach cancer before symptoms
appear.
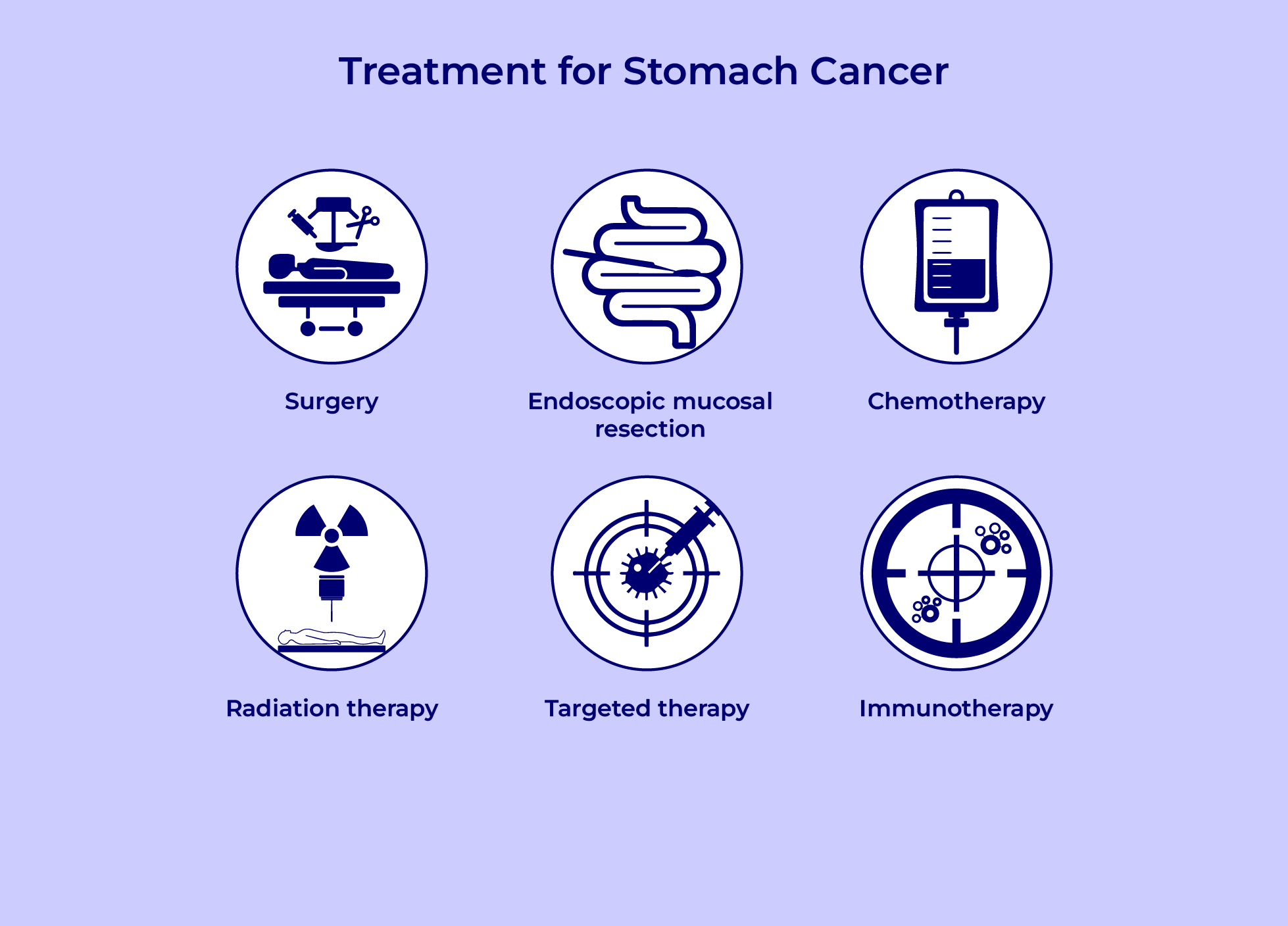
Treatment
- The stage and location of the stomach cancer
will determine the therapies:
- Removing small cancers from the stomach lining.
- Removing part of the stomach
- Removing the entire stomach
- Removing lymph nodes to look for cancer
- Surgery