What is Esophageal Cancer?
- Esophageal cancer develops when cancerous cells
begin to grow in the lining of
the esophagus i.e, a long, hollow tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
It allows the swallowed food to move from the back of the throat to the
stomach, so that it can be further digested. The inner layer of the esophagus is
where the cancer typically first displays itself, and it also tends to spread to
other layers of the esophagus and other regions of the body (metastasis)
through the lymphatic system (consisting of different types of vessels which
specifically drain lymph from the tissues into the blood).
Men are more prone to esophageal cancer than
women. It is ranked as the
sixth most common cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Different geographical
locations lead to variation in the incidence rates of the disease. Increase in
number of cases in certain regions may be due to tobacco and alcohol use or
due to particular nutritional habits and obesity.
Early-stage esophageal cancer can be treated
with surgery, as to remove the
tumor or relieve the symptoms whereas advanced or later stage esophageal
cancer can be treated using chemotherapy, radiation therapy and
immunotherapy.
There are two forms of esophageal cancer:
-
Squamous Cell Cancer: A tumor that originates with squamous cells and
forms the surface of the skin and lining of hollow organs in the body.
- Adenocarcinoma: A malignant type of tumor that develops in the areas
at the bottom of the esophagus and at the junction where the
esophagus joins the stomach as it is lined with columnar cells.
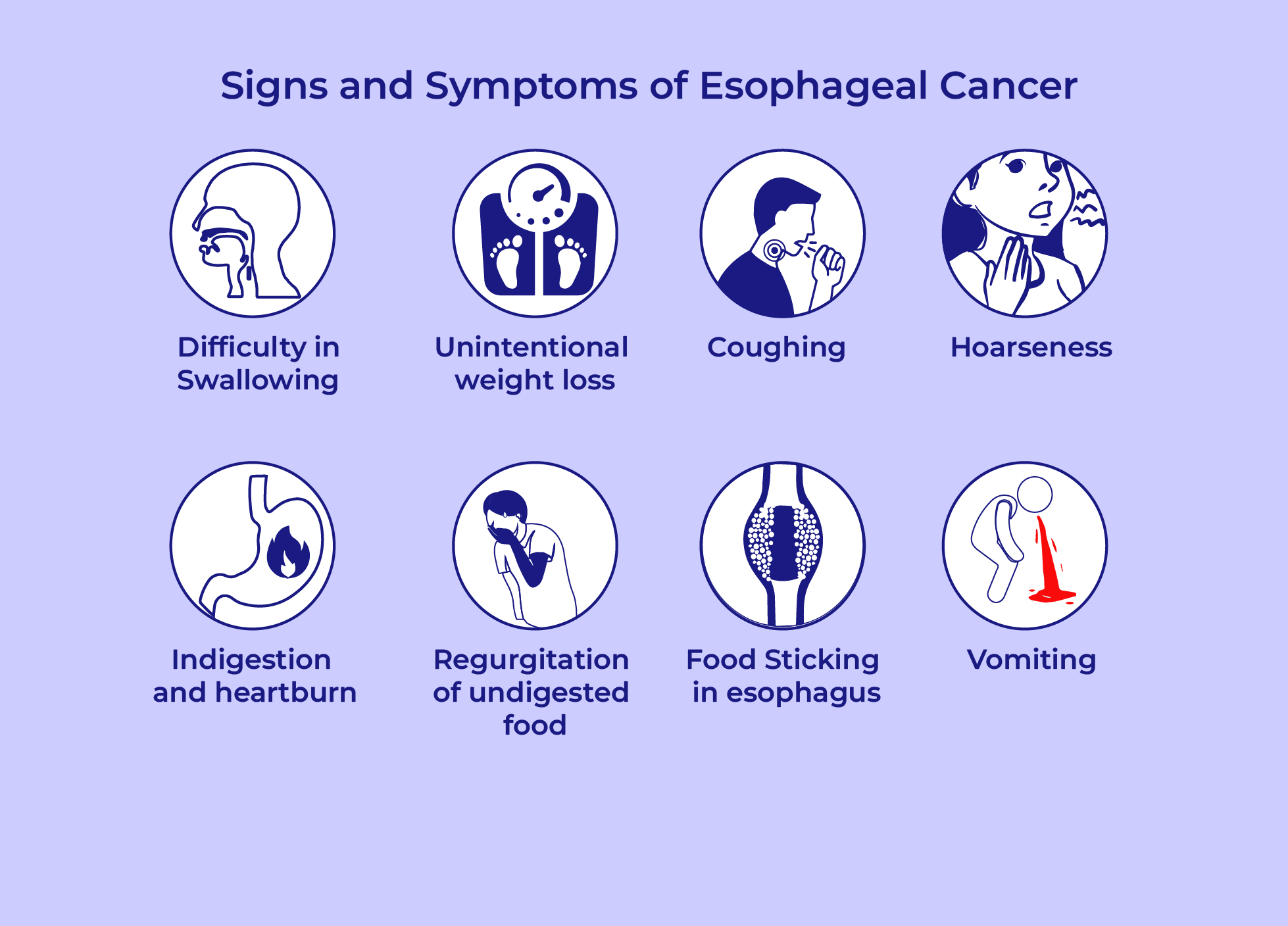
What are the signs and symptoms of Esophageal Cancer?
- Early stages of esophageal cancer may not have
any apparent symptoms,
however advanced stages show the following signs and symptoms:
-
Difficulty or pain when swallowing
- Unintentional weight loss
- Coughing
- Hoarseness
- Indigestion and heartburn
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Food Sticking in esophagus
- Vomiting blood or passing old blood with bowel movements
What are the main causes of esophageal cancer?
- The exact cause of this disease is not known
but the factors that contribute
in increasing the chance of developing esophageal cancer are:
-
Use of Tobacco:This consists of smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco
- Alcohol Use:The risk is increased to many folds with heavy
alcohol consumption.
- Obesity:Inflammation caused in obese people by being overweight can
lead to the formation of cancer.
- Barrett's esophagus and chronic acid reflux:Untreated acid reflux can
cause changes in the cells at the lower end of the esophagus. People also
suffering from long term heartburn are at a greater risk of esophageal cancer.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV):HPV is a common virus which is
responsible for causing changes in the vocal cords, mouth, hand, feet and genital tissues.
- Occupational exposure to certain chemicals:Exposure to dry cleaning
solvents for a long time increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
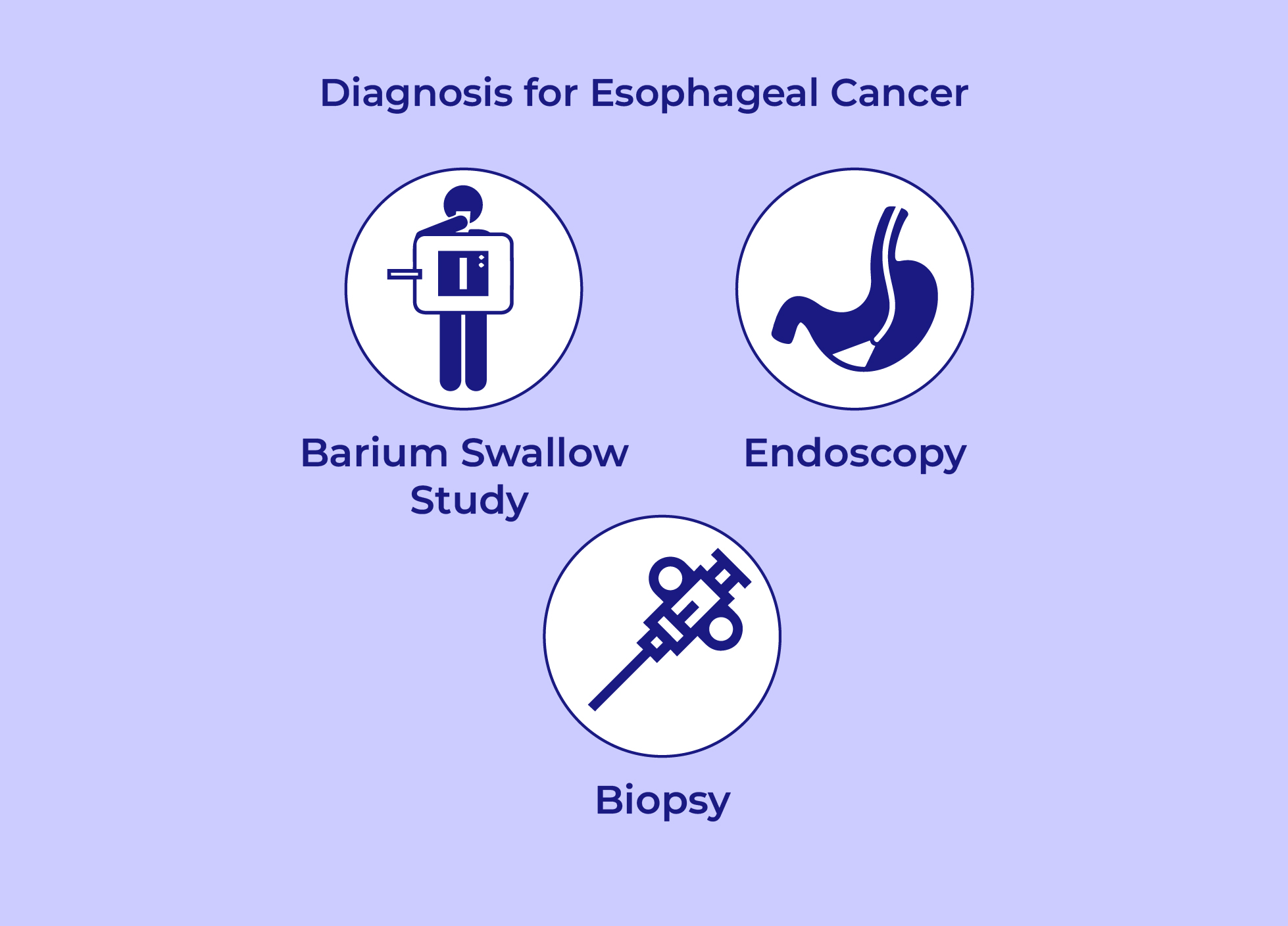
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
- The various diagnostic tests for esophageal
cancer are:
-
Barium Swallow Study:A liquid containing barium is given to the patient to swallow and
then an X-
Ray is performed. The esophagus is coated with the barium present in the
liquid to show any changes to the tissue on the X-Ray.
- Endoscopy:A flexible tube connected with a video lens is passed down
the throat into the esophagus by your doctor to check for cancer or areas of irritation.
- Biopsy: (Using a sample of your tissue for testing):An endoscope is passed down your
throat into your esophagus to collect a
suspicious tissue sample. It is then sent to the laboratory to check the
presence of cancer cells.
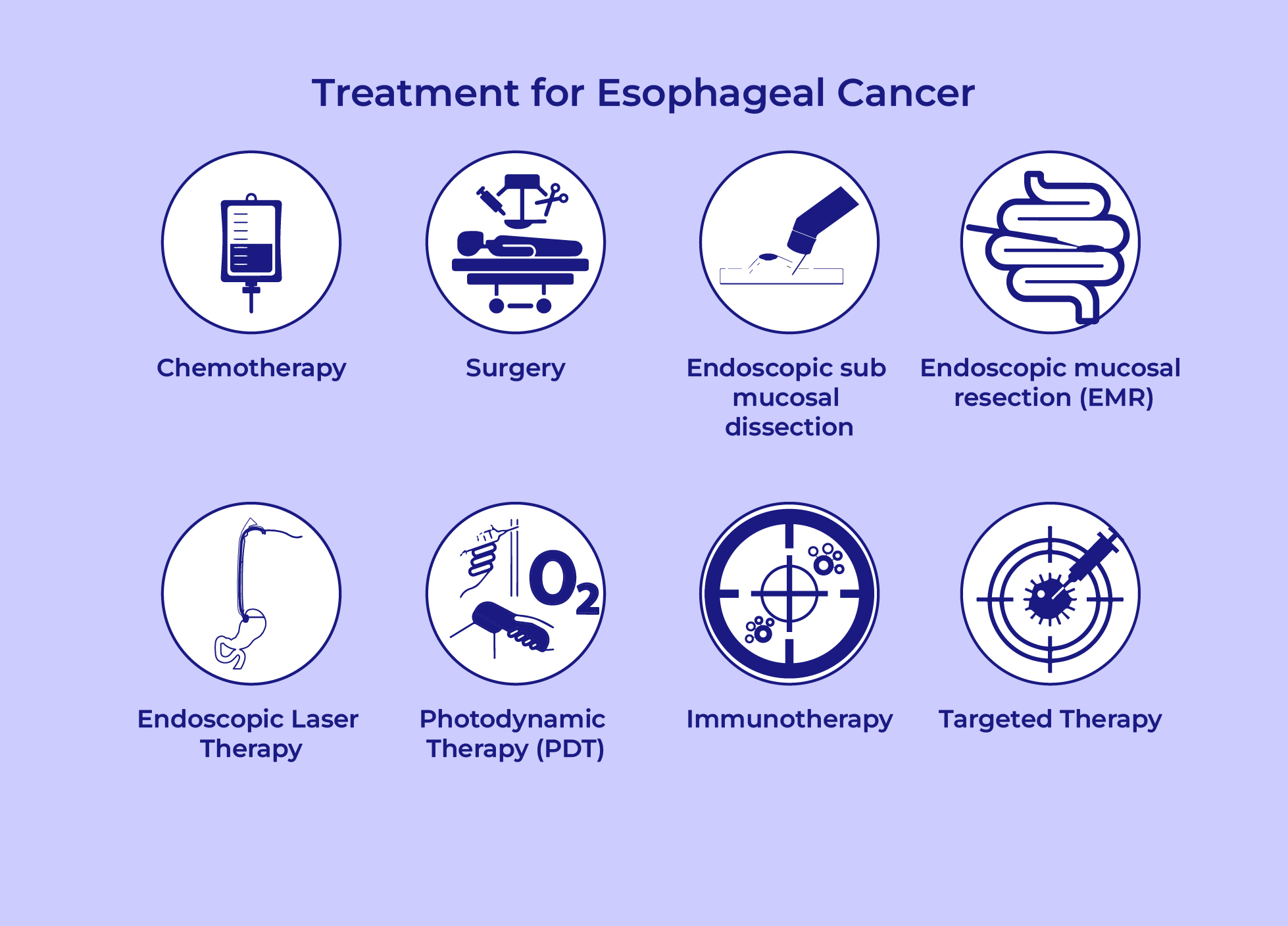
What are the available treatment options for esophageal cancer?
- The treatment options given to the patient
depend entirely on the type of
cells involved in cancer, the stage of the cancer and overall health.
-
Surgery:The Surgery can be a preferred for revoking cancer cells, either
alone or in combination with other treatments:
- Removal of very small tumors:If the tumor is within the operatable
range and confined to the superficial layer of the esophagus only,
then an endoscope can be used to remove the cancer as well as the
healthy tissue that surround it to avoid further spreading.
- To remove a portion of the esophagus (esophagectomy):During
esophagectomy, an entire portion of the esophagus that contains
cancer is removed along with an upper part of the stomach and
nearby lymph nodes. The remaining portion of the esophagus is
reconnected back to the stomach.
- To remove part of your esophagus and an upper part of your
stomach:It is also called as esophagogastrostomy, where a part of
your esophagus along with a larger part of the stomach and nearby
lymph nodes are removed. The remaining part of the stomach is
reattached to your esophagus. A part of your colon can be used to
join the two.
Esophageal cancer surgery is a risky procedure, which carries risk of
serious complications, like infection, bleeding and leakage from the
area where the remaining esophagus is reattached to the stomach.
- Chemotherapy:Chemotherapy helps in killing of the cancer cells or
stops their growth.
- Endoscopic sub mucosal dissection (ESD):To treat very early-stage esophageal cancer.
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR):The cancer in the mucous lining is removed using this
procedure.
- Endoscopic Laser Therapy:The tumors in the esophagus can sometimes
get obstructive, hence making it hard to swallow. With the help of this
treatment, the symptoms can be maintained easily.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT):Photosensitizers are the drugs that
destroy the tumor. The killing of cancer cells is done when light activates
these drugs, thus creating a chemical reaction.
- Immunotherapy:Immune checkpoint inhibitors are used in this
treatment. The response to the esophageal cancer cells is restored with
the help of these drugs.
- Targeted Therapy:Certain esophageal cancer cells carry an extra
quantity of HER2 protein. It is essential for the growth of cancer cells.
Therefore, the drugs targeting HER2 proteins are used in the targeted therapy.